What Is Inflammation and How to Manage It as You Age
As we age, we often notice the emergence of wrinkles, aches, and pains, accompanied by an increase in inflammation within our bodies. Inflammation, while common, can signal underlying health concerns. However, there are proactive measures one can take to manage inflammation, such as participating in comprehensive workouts like the Curves Circuit and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into one’s diet. Let’s delve into the essence of inflammation—its origins, its impact on the body, and strategies for mitigating its effects.
What is Inflammation?
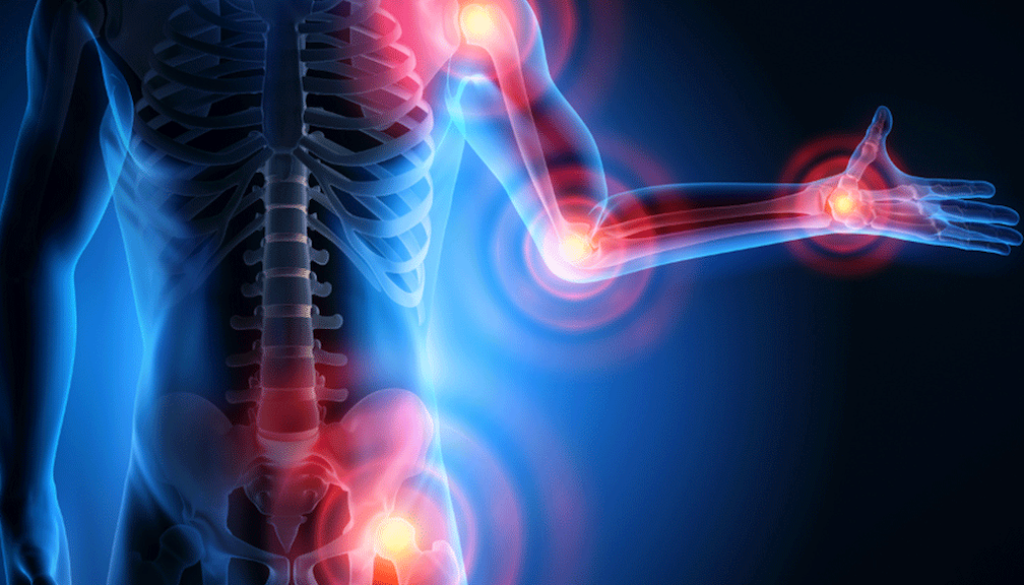
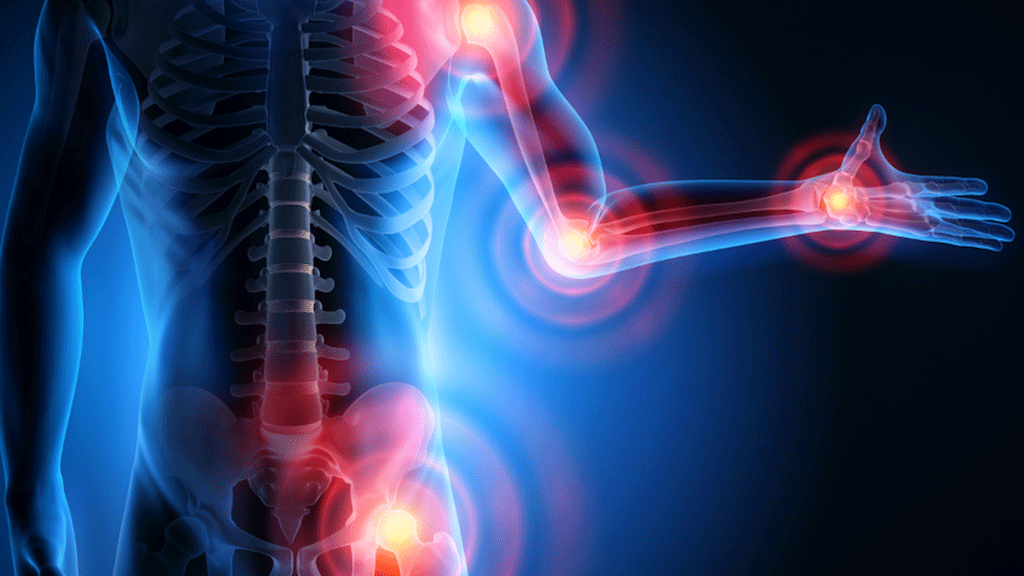
Inflammation serves as your body’s defence mechanism, aiming to mend injuries or combat intruders like bacteria, viruses, or chemicals. Upon encountering such threats, your immune system dispatches cells to initiate an inflammatory reaction, intending to confine and commence the healing process. This inflammatory process manifests as pain, redness, swelling, or bruising. However, inflammation isn’t confined to the site of injury; it can extend to other body parts, causing more harm than good.
There exist two primary forms of inflammation: acute and chronic.
Acute inflammation occurs in response to sudden injuries or invasions, such as a paper cut on your finger. In an effort to heal the wound, your body mobilises inflammatory cells to the affected area, leading to symptoms like pain, swelling, redness, and warmth.
On the other hand, chronic inflammation persists beyond the initial injury or invasion, with your body sustaining the inflammatory response over the long term. Symptoms of chronic inflammation encompass joint pain, weight gain, skin rashes, abdominal discomfort, fatigue, chest pain, fever, and oral ulcers.
The Danger of Chronic Inflammation
Unchecked chronic inflammation poses a significant threat, gradually harming your body and elevating the risk of various diseases and conditions. It can inflict damage on arteries, organs, and joints, potentially resulting in the accumulation of fatty deposits around your arteries.
Addressing chronic inflammation typically begins by combating lifestyle habits that could exacerbate it, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, weight gain, and sedentary behaviour. Additionally, certain medications can assist in combating inflammation, along with adhering to an anti-inflammatory diet.

How to Reduce Inflammation:
Here are several strategies to help alleviate inflammation in your body:
Manage Stress: Psychological stress has been linked to inflammation, as prolonged elevation of the stress hormone cortisol can induce inflammatory effects. To mitigate stress:
Maintain a regular exercise regimen, such as the Curves Circuit.
Explore mindfulness practices or deep breathing techniques, as offered in our Curves at-home workout program, MyCurves On Demand Audio Category.
Incorporate yoga sessions from MyCurves On Demand’s Balance Category into your routine.
Increase physical activity
Engaging in low-impact full-body exercise routines like the Curves Circuit may initially trigger acute inflammation following your workout, but it yields long-term anti-inflammatory effects. Furthermore, exercise promotes an increase in serotonin levels, aiding in the reduction of psychological stress. For those utilising MyCurves On Demand, classes from the Body Basics and Balance Categories offer excellent low-impact options.
Reduce alcohol intake
Alcohol consumption, particularly in high amounts, can cause inflammation in your gut and throughout the rest of your body. To prevent inflammation that may result from alcohol, drink no more than one drink a day if you are a woman, and no more than two drinks a day if you are a man.

Quit smoking
It’s common knowledge that smoking is one of the worst habits for your health, primarily because it boosts inflammation. If you smoke cigarettes, quitting is imperative.
Lose weight
Weight gain triggers inflammation, while inflammation, in turn, contributes to further weight gain. Breaking free from this detrimental cycle entails committing to a consistent full-body workout regimen such as the Curves Circuit, coupled with adopting a weight loss eating plan rich in anti-inflammatory foods.
Anti-inflammatory Diet and Meal Plans
Certain foods can exacerbate inflammation, commonly found in the modern American diet:
1. Refined carbohydrates like candy, pastries, and white bread
2. Red meat such as burgers and steaks
3. Processed meats like sausage and hot dogs
4. Sweetened beverages including soda
5. Fried foods such as French fries
6. Margarine, lard, and shortening.
Conversely, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet can help mitigate inflammation:
1. Whole grains like brown rice, oatmeal, and barley
2. Fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel
3. Flaxseeds which also contain omega-3 fatty acids
4. Blueberries and cherries high in antioxidants
5. Edamame containing isoflavones and omega-3 fatty acids
6. Green tea is abundant in anti-inflammatory flavonoids.